
Ssh copy key how to#
Whether you’re a system administrator managing multiple Ubuntu servers or a developer looking to streamline your workflow, understanding how to copy SSH keys can save you time and enhance your security. The simplest way to copy your public key to an existing server is to use a utility called ssh-copy-id. We also discussed alternative methods for those who prefer a different approach. In this article, we explored the easiest way to copy SSH keys to another machine in Ubuntu using the ssh-copy-id command. If the ~/.ssh directory doesn’t exist, you’ll need to create it and set the appropriate permissions. This command reads your public key ( ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub), logs into the remote server, and appends the key to the ~/.ssh/authorized_keys file. You can do this by running: cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub | ssh 'cat >. If for some reason you cannot use the ssh-copy-id command, you can manually copy the public key. In this command, is the port number used by the remote server. You can also specify a username if you don’t want to use the. To copy your key to a server, run this command from the client: ssh-copy-id hostnameorIP. The key is the file idrsa.pub previously created with SSH keygen utility. If the remote server uses a port different from the default ( 22), you can specify the port number: ssh-copy-id -p " To use the key pair for SSH authentication, you’ll need to copy the public key to a server. If you have multiple identities or want to specify a different identity file, you can use the -i option: ssh-copy-id -i identity_file this command, identity_file is the path to your identity file. To copy your default identity’s public key to the remote host, run: ssh-copy-id this command, user is your username on the remote machine and is the hostname or IP address of the remote machine. This command is part of the openssh-client package, which is installed by default on Ubuntu.
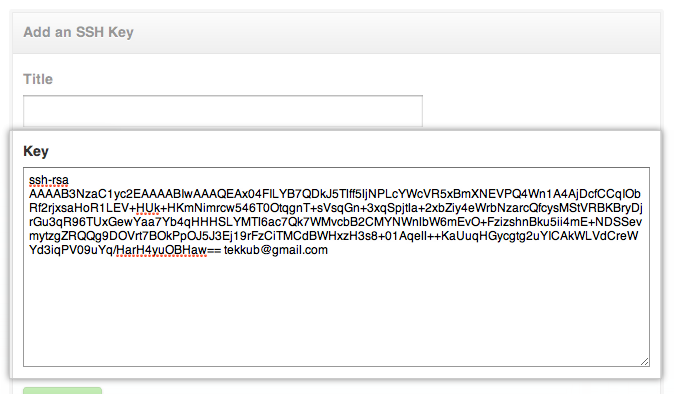
The easiest and most recommended way to copy your SSH keys to another machine is by using the ssh-copy-id command. You will be asked to enter a passphrase, which is optional and adds an extra layer of security. This command will generate a new RSA key pair. If you haven’t already generated your SSH keys, you can do so by running the following command: ssh-keygen -t rsa
Ssh copy key install#
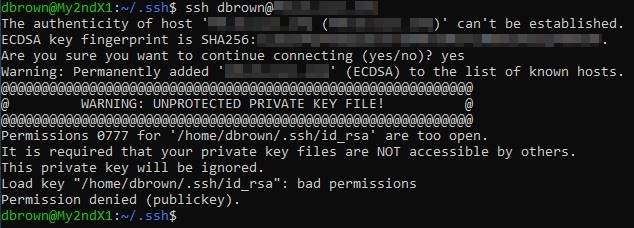
If not, you can install it by running the following command: sudo apt-get install openssh-server Generating SSH Keys Installing SSH in Ubuntuīefore we start, make sure you have SSH installed on your Ubuntu machine. Only the corresponding private key can decrypt this message, proving the client’s identity. The SSH server can verify the client’s identity by creating a new, unique challenge message and encrypting it with the public key. A private key, which is secret, and a public key, which is shared. SSH keys are a pair of cryptographic keys that can be used to authenticate to an SSH server as an alternative to password-based logins.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
